

BREATH uses the principle of sublimation to transform biomass, waste plastic and various other organic materials into Syngas (synthesis gas) and then use it in an endothermic engine that, when connected to an alternator, produces electricity. The post-combustion gases of the endothermic engine are conveyed and sent in part into the reactor itself and partly into the catalysts of the CO2 for the sequestration thereof. At the same, the condensansation liquid contained in the combustion materials is collected and then sent to electrolysers that capture the hydrogen. CO2 and hydrogen are then introduced into the methanation reactor in which the reaction of Sabatier (CO2 + 4H2 = CH4 + 2H2O) takes place. Therefore, as output, we have synthetic gas and water.
• Working temperature 1250° • No combustion • Zero Dioxins • No harmful emissions on atmosphere • Wide range of eligible feedings • Reduction of costs for kwe energy production • Long-term 24/24H operational availability • Modularity • Remote assistance (plc supervisor) • Designed & Made in Italy

An idea becomes reality only when "you" are aware of you, whoever is around you is not just a presence but part of a whole.
The intrinsic potential of Breath is its adaptability, its versatility to any site without too many difficulties since the space required is considerably reduced and no particular geographical features are required. All types of organic material and plastics can be processed, thus avoiding further accumulation in landfills that are already on the verge of collapse.
Breath converts the fuel materials into Syngas, and water, which are then used to produce electricity and heat. After the energy production, the exhaust gases from the process are processed in a second reactor, producing water and synthetic methane.

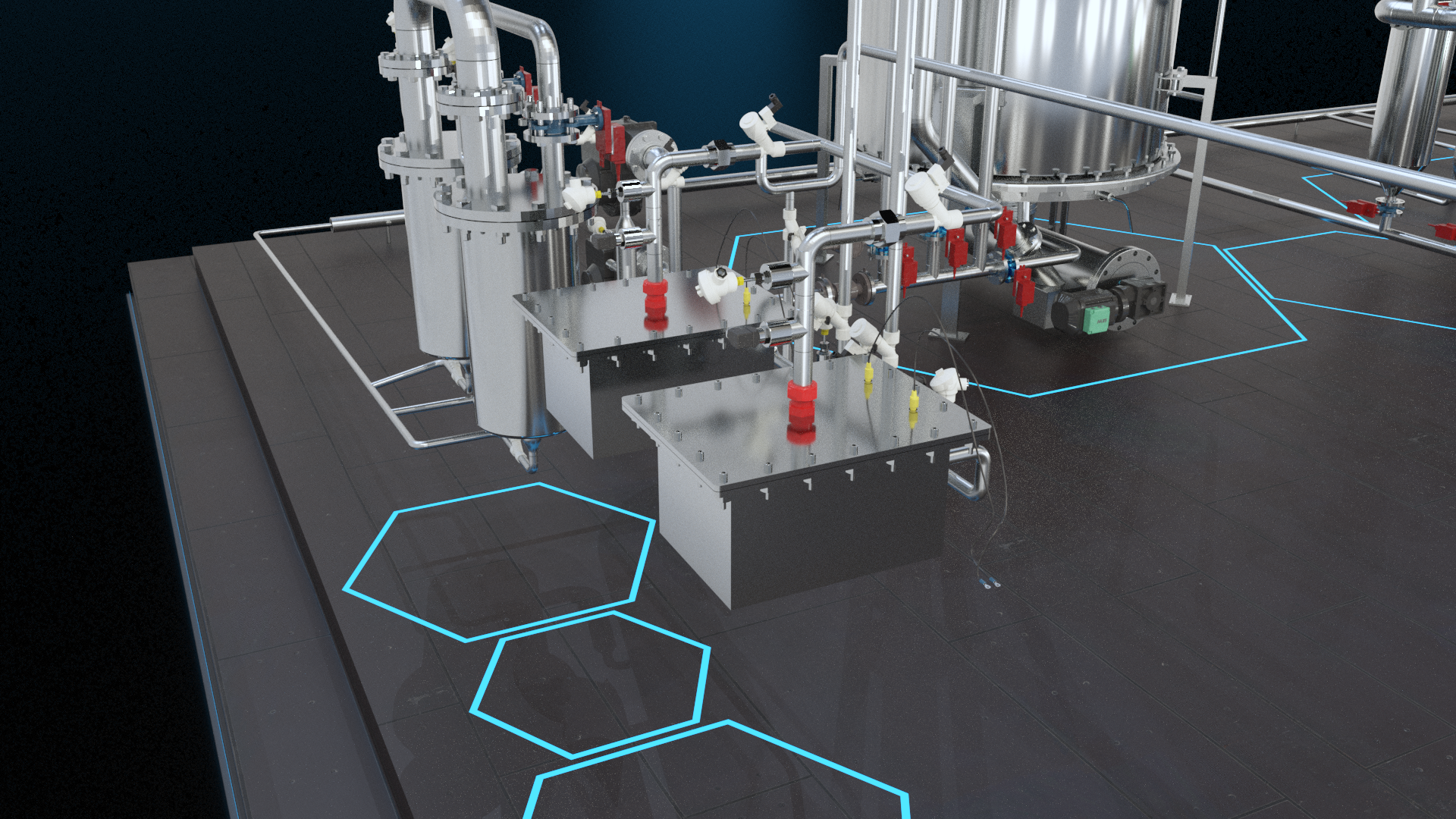 ↑ 2. Methane synthesys. The excess condensation fluid can be used for industrial or agricultural purposes, but the remaining part of the condensation fluid
is sent to the electrolyser units, which produce hydrogen (H2). At the same time, the post-combustion gases originating from the engine
are conveyed to a catalyst, which sequesters the carbon dioxide (CO2). The CO2 and the H2 are then sent to a second reactor where,
by making use of Sabatier’s reaction, methane (CH4, purity >92%) and water (H2O) are produced. The remaining fraction of the post-combustion gases (N2, H2O)
is then released in the environment.
↑ 2. Methane synthesys. The excess condensation fluid can be used for industrial or agricultural purposes, but the remaining part of the condensation fluid
is sent to the electrolyser units, which produce hydrogen (H2). At the same time, the post-combustion gases originating from the engine
are conveyed to a catalyst, which sequesters the carbon dioxide (CO2). The CO2 and the H2 are then sent to a second reactor where,
by making use of Sabatier’s reaction, methane (CH4, purity >92%) and water (H2O) are produced. The remaining fraction of the post-combustion gases (N2, H2O)
is then released in the environment. 
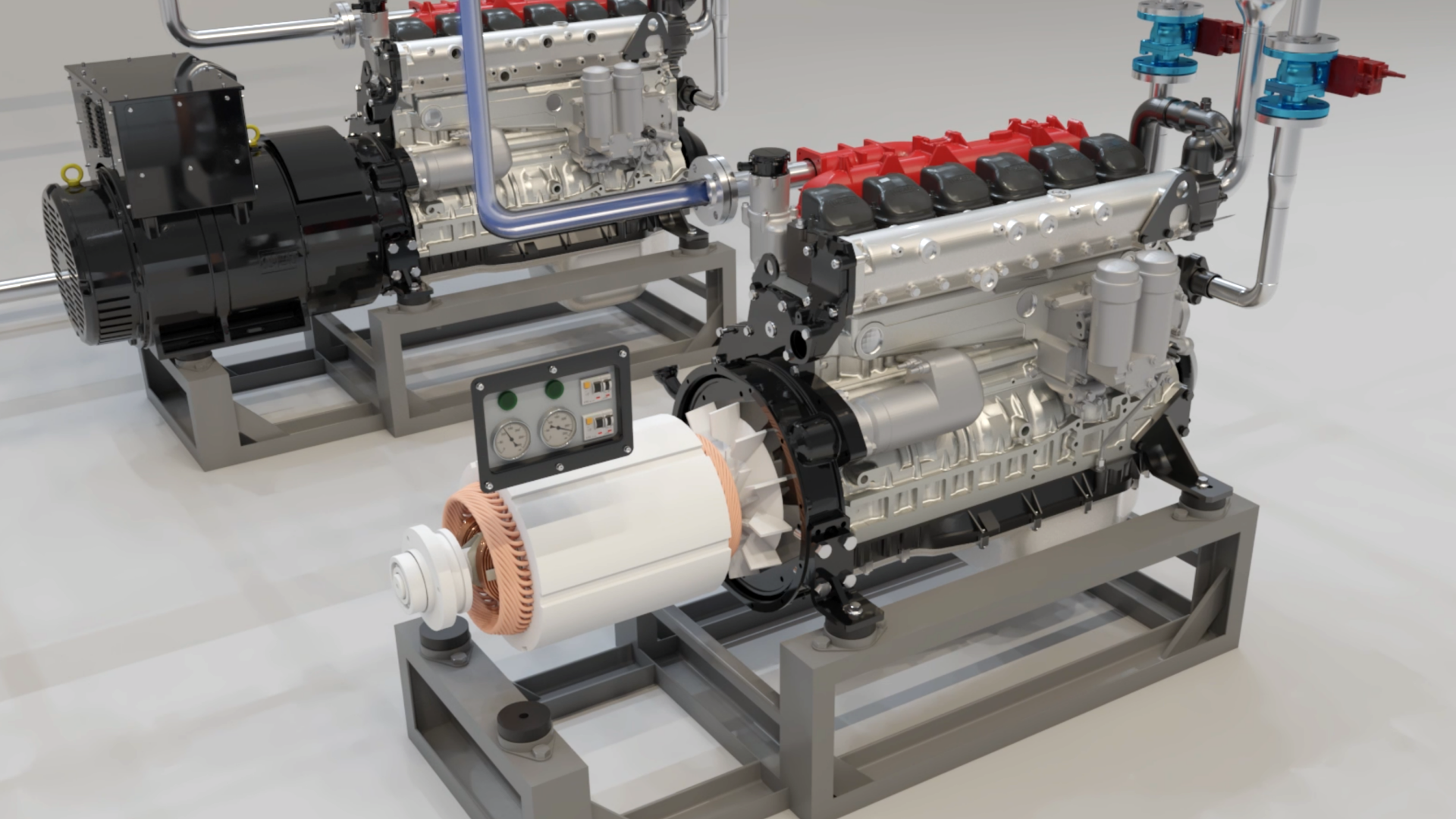 ↑ 4. Energy production. After the filtration, if the desired composition is achieved, the Syngas is fed into an internal combustion engine,
which produces electricity. Part of the condensation fluid is used in the heat exchangers to recover the thermal power generated during the reactor activity.
Through this process, steam and hot water are produced. Breath works by regulating the process speed in order to always reach
an energy production target of 125 kWeh & 235 kWth at regimen.
↑ 4. Energy production. After the filtration, if the desired composition is achieved, the Syngas is fed into an internal combustion engine,
which produces electricity. Part of the condensation fluid is used in the heat exchangers to recover the thermal power generated during the reactor activity.
Through this process, steam and hot water are produced. Breath works by regulating the process speed in order to always reach
an energy production target of 125 kWeh & 235 kWth at regimen.